Are you ready to get your garden off to a successful start this year?
With the 2023 update to the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, you can now know how these changes will affect your garden.
This updated map will help you determine which plants will thrive in your climate and give you tips on how to make the most of the updated zones.
So join us on this journey to explore the changes to USDA Plant Hardiness Zones and learn what you need to know for successful gardening this year.
Key Takeaways
- Growing zones indicate a plant’s hardiness based on climate and help determine if a plant can survive the coldest winters in a region.
- The USDA Hardiness Zone Map does not address summer temperatures and only focuses on average coldest winter temperatures.
- Urban areas may have a warmer growing zone due to the urban heat island effect, while areas with more vegetation in cities may have cooler temperatures.
What Are The USDA Plant Hardiness Zones?
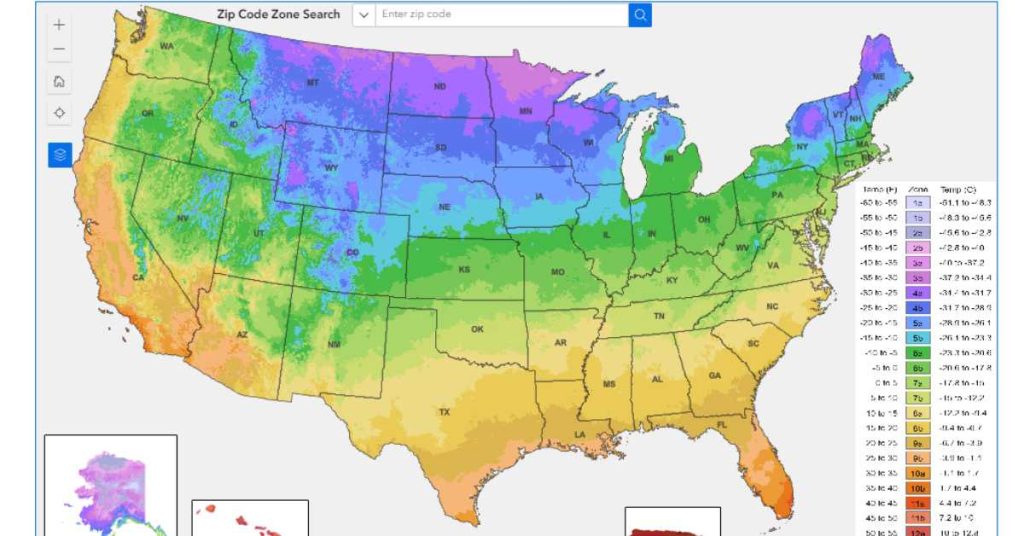
You may be familiar with USDA Plant Hardiness Zones and their importance for gardening. These zones help gardeners determine if a plant can survive the coldest winters in their region, based on the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone map. They indicate a plant’s cold tolerance and are determined from climate zones and 30-year average winter temperatures.
The zones use 10-degree Fahrenheit intervals and half-zones based on 5-degree differences. The most recent map was updated in November 2023, accounting for changes in average annual lows. Urban areas may have a warmer zone due to the urban heat island effect.
Northern growers may enjoy a longer growing season, while southern growers may need to protect plants from extreme heat. Overall, the USDA map shows a general shift of about 2.5°F warmer annual temperatures.
Do USDA Growing Zones Matter?
Understanding USDA growing zones is essential for gardening in any region. Knowing the hardiness zone of your area can help you decide which plants are best suited for your climate and ensure the success of your garden.
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone map provides important data about the average annual low temperatures in your area, so it’s important to take note of the changes in your growing zone.
How Are The Hardiness Zones Determined?
Knowing your USDA plant hardiness zone is essential for successful gardening.
The process of determining zones is based on a variety of factors and is mapped by the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map.
The map uses data from over 13,000 weather stations to determine the average annual lows.
These zones are further broken down into 10-degree Fahrenheit intervals (zone 1-13b) as well as half-zones based on 5-degree differences.
The most recent map was updated in November 2023, providing more accurate and detailed zone delineations.
To ensure zone accuracy, it’s important to stay up-to-date on the latest updates and combine information from various sources.
2023 Changes to USDA Plant Hardiness Zones: Overall Trend
The overall trend in growing zones shows a general shift of about 2.5°F warmer annual temperatures across the U.S. This has impacts on gardening, as well as regional gardening challenges due to climate change effects.
Approximately half the U.S. has shifted one-half zone warmer, while others remain in the same half-zone due to subtle shifts in average annual low temperatures. Northern growers may be able to plant warmer-weather perennials and enjoy a longer growing season, while Southern growers may need to protect plants from extreme heat and avoid heat-sensitive temperate perennials.
When selecting plants for your garden, it’s important to consider climate change effects and combine information from various sources.
Zone Changes in Cities and Florida
Urban areas may experience a warmer growing zone due to the urban heat island effect. The impact of urban heat can be felt from coast to coast, with cities like New York, Los Angeles, and Chicago experiencing an average of one full zone warmer than their surrounding areas.
This effect is felt even more keenly in Florida, where climate change has resulted in a shift from zones 8-9 to 10-1. Gardeners must adapt their strategies for growing in warmer zones, while blueberry farmers face challenges from the shift in southern zones.
But in the northeast, the warmer temperatures provide opportunities for crop diversity. These changes to USDA plant hardiness zones underscore the importance of understanding climate shifts and the need for adaptation.
Zone Changes in Specific Regions
Diving into specific regions, you can see how the zone changes are impacting growers.
The South is feeling the shift from zones 7-8 to 9-10, causing concern for crops like blueberries.
In the Northeast, gardeners are pushing into warmer zones, allowing for crops like sweet potatoes and long-season outdoor peppers.
Northern Florida is becoming more subtropical, moving from zones 8-9 to 10.
Urban areas may have a warmer growing zone due to the urban heat island effect.
Alaska benefits from the new map’s detailed microclimate considerations and resolution.
Minnesota shifted to warmer zones, while Illinois experienced a northward shift.
These zone changes affect agriculture, gardening, climate shifts, plant selection, and microclimates.
It’s important to keep up with the changes and adjust your garden accordingly.
Zone Changes in the South
You may have seen warmer winters in the South, shifting zones 7-8 to 9-10, which affects crops like blueberries. Southern growers from Texas to Georgia are accustomed to scorching summers, but the warmer winters are a concern. Varieties like Southern highbush blueberries thrive with fewer chill hours and may have to replace the berry bushes in warming zones.
The benefits of the warmer climate include:
- Longer growing seasons for warm-weather crops.
- Heat-sensitive temperate perennials may stay alive longer.
- Expansion of subtropical plants into northern regions.
Southern growers should be aware of the climate shifting and the effects on their crops. It’s important to understand the changes and take the necessary steps to ensure plants survive the shifting growing zones.
Zone Changes in the Northeast
Building on the changes in the South, the Northeast has also experienced warming trends that push northeastern gardeners into warmer zones. This has an impact on the plants that can be grown, providing new crop possibilities.
However, rising pest pressure is a concern as insects aren’t being knocked out by cold temperatures.
Microclimate considerations are also key for this region, as areas with more vegetation may have temperatures at least a half zone cooler.
Perennials suitable for Minnesota gardens may now be suitable in the Northeast, while Southern growers may need to protect plants from extreme heat and avoid heat-sensitive temperate perennials.
Zone Changes in Alaska, Minnesota, and Illinois
Discovering the zone changes in Alaska, Minnesota, and Illinois can help gardeners determine which plants will thrive in their area. In Alaska, the USDA map reveals a warmer climate with microclimate considerations. Northern regions have shifted by a half or complete zone due to warming temperatures.
In Minnesota, most of the state has shifted to warmer zones, while in Illinois, a northward migration has occurred with 6a-6b progressing to 7a-7b. These changes may impact the perennials grown in each area and require:
- Understanding USDA zone shifts
- Adapting to warmer winter temperatures
- Planting varieties suitable for the zone
Frequently Asked Questions
How Often Are USDA Plant Hardiness Zones Updated?
The USDA Hardiness Zone Map is updated every 10-15 years to reflect climate variability, watering requirements, soil amendments, sun exposure and pest control. It’s important to consider all these factors when choosing plants for your garden.
What Precautions Should I Take When Planting in a Zone That Has Experienced a Shift?
When planting in a shifted zone, consider soil type, planting seasons, sun exposure, water requirements, and pest control. Research the right plants for your area and make sure you understand their climate needs. Adjust your planting schedule and techniques accordingly for successful gardening.
What Are the Long-Term Implications of Global Climate Change on Growing Zones?
Global climate change has long-term implications on growing zones, such as changes in climate variability, soil composition, water availability, and the emergence of invasive species. Pest management strategies will need to be adjusted to accommodate these changes.
Are There Any Other Factors Besides Average Winter Temperatures That Should Be Considered When Choosing Plants?
When choosing plants, consider factors like soil quality, water availability, light exposure, pest control, and climate variability. All of these can affect a plant’s success and should be researched and accounted for in order to ensure the best chance of success.
How Can I Tell if a Plant Is Suitable for My Area?
To determine if a plant is suitable for your area, consider container gardening, soil preparation, native plants, water requirements, and sun exposure. Research these factors before purchasing and planting to help ensure success.
Conclusion
No matter where you live, the 2023 changes to the USDA Plant Hardiness Zones are sure to have an impact on your gardening plans. By understanding the changes and how they affect your region, you can ensure success in your garden this year.
The tips we’ve provided in this article will help you make the most of the updated zones and get your garden off to the best possible start.
So don’t wait, start planning your garden today and make the most of the 2023 changes to the USDA Plant Hardiness Zones.





